Education About Diamonds for Buffalo, NY
When you are thinking engagement rings or earrings and really want something special, nothing says it better than diamonds.
The Diamond is the birthstone of April and the anniversary gemstone for the 10th and 60th years of marriage. Since diamonds are composed of a single element, they are the purest of all gemstones. Diamonds were discovered in India in 500 B.C., and the name “diamond” comes from the Greek word “Adamas” which means unconquerable – suggesting the eternity of love.
The ancient Greeks believed diamonds were hardened dew drops, splinters from the stars or crystallized lightning and they cherished diamond jewelry as a symbol of love. Today, the gem-grade diamonds are used to make fine jewelry and engagement rings. The industrial-grade diamonds are used mainly for cutting and polishing. A diamond is the hardest substance known to humankind, and is made of a crystallized carbon that has unique powers of light reflection.
The Structure of a Diamond

Symmetry is a grading term for the exactness of shape and placement of facets. Variations in symmetry include off-center culets and tables, poor facet alignment, misshapen facets, out-of-round girdles, and wavy girdles.
The Value of a Diamond: The Four C’s
Diamond Cut
Reflection

A) When a ray of light touches the surface of a diamond, part of the light is reflected back, this is external reflection.
Refraction

B) The rest of the ray penetrates the stone and is then reflected toward the center of the diamond. This is known as refraction.
Dispersion
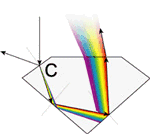
C) The ray of light is reflected to the surface, where it is seen as the colors of the spectrum. This is known as dispersion.
The Cut is the factor that determines the brilliance of a diamond. A classic round brilliant cut diamond has 58 facets : 33 on the top, 24 on the bottom, and the culet (1 point at the bottom). Each of the diamond’s facets must be placed in exact geometric relation to one another when the stone is being cut. Quality diamonds must be properly cut and not “spread”, which means that the proper proportions are compromised to make the diamond weigh more.
Diamond Clarity

- FL-EF | Flawless or Internally Flawless. No internal inclusions.
- VVS1-VVS2 | Very Very Small inclusions. Very difficult to see under 10x magnification.
- VS1-VS2 | Very Small inclusions. Can be seen under 10x magnification and in some cases to the naked eye.
- SI1-SI2 | Small inclusions. Can bee seen under 10x magnification and may be visible to the naked eye.
- I1-I2-I3 | Imperfect. Inclusions are visible under 10x magnification and in most cases to the naked eye.
The Clarity of a diamond is based on the number, location, size, and type of inclusions found in the stone. An inclusion is an imperfection or trace mineral in the stone that is visible under the magnification of a jeweler’s loupe. The fewer inclusions the diamond has; the clearer, more brilliant and more expensive the diamond will be. A “Flawless” diamond is one that has no inclusions and is extremely rare and valuable.
Diamond Color

Colorless and near-colorless diamonds are the most valuable. Though most diamonds may appear colorless to the naked eye, the majority of diamonds contain slight traces of yellow or light brown when viewed under a jeweler’s loupe. Depending on the stone’s size, a single increase in color grade can boost the value of a diamond by thousands of dollars per carat. A traditional engagement diamond is usually colorless or near-colorless.
In nature, diamonds can also occur in shades of red, pink, blue, green and deep yellow – These are called “Fancy diamonds”. In the United States and around the world colorless diamonds are graded on an alphabetical scale, introduced by the Gemological Institute of America (GIA). “Colorless” or “rare white” diamonds are of color grades D, E and F. Diamonds of color grade D are very rare, and extremely valuable.
Diamond Carat Weight
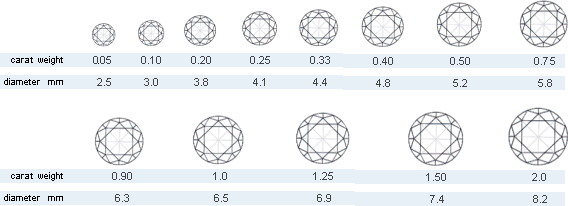
The weight of a diamond is measured in carats (ct.). Each carat is divided into 100 points. For example: 1ct.= 100 points, 1/2 ct. = 50 points, etc. The carat weight alone is almost meaningless unless you also consider the cut, clarity and color of the diamond. A large diamond is not very valuable if it lacks brilliance, purity and high-grade color.
However, since larger stones are rarer than smaller ones, diamond value rises exponentially with carat weight. Therefore, a diamond weighing 3.0 carats, will always be worth more than three 1.0 carat stones of the same quality. No two diamonds are exactly alike, and you must weigh all of the factors – color, cut, clarity and carat weight – when making your diamond jewelry buying decision.
